ABC analysis was defined by the italian economist Pareto (1848-1923) and, with this application, allows to manage the product stocked in a warehouse.
Class A items are those whose sum equals 80% of the feature to be analyzed; B items for the further 15%, and C items for the remaining 5 %.
The various features than can be taken into account are:
- Cost of Goods Sold (annual)
- Picked quantity
- On hand in value
- On hand in quantity
- On hand in volume
- Profit
- Picked lines
Statistically point of view, the A items can be about 20 % of the totality, B items about 30 %, and C items the remaining 50%.
As a conseguente, it is produttive to keep our attention on the A items first (with only 20 per cent of the items we master 80 per cent of the considered feature), and to leave the C items just at the end of the analysis (also if they are about half of the totality), because they count the 5 per cent of the feature taken into consideration.
ABC cross analysis
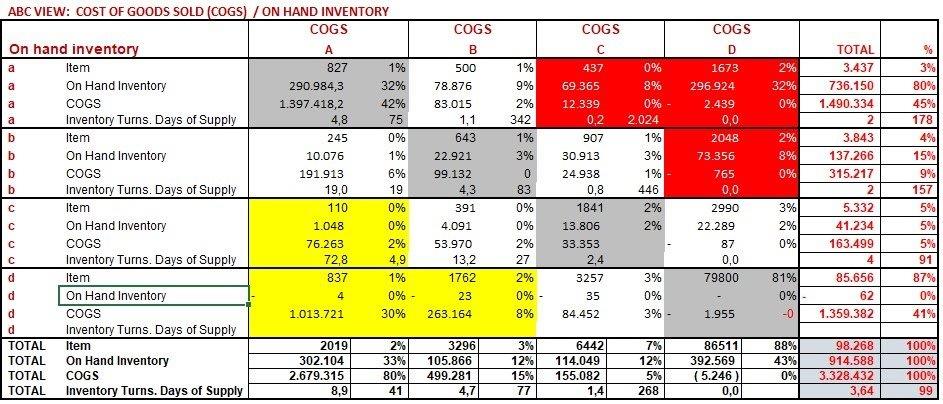
The application elaborates an ABC cross analysis, the output are reports and seven interactive matrices, where two features are crossed, such as:
- COGS/On hand in value
- Picked quantities/On hand in quantity
- COGS/Profit
- COGS/Picked lines
- Picked quantities/Picked lines
- On hand in quantity/Picked lines
- Picked volumes/On hand in volume
The objective of these seven views is as follow
Views 1 and 2: to select the items with an excess inventory and at high risk of stockout; furtherly you have the inventory turn and days of supply. They are useful to correct the average inventory level of the above items.
View 3: to select items with negative or low profit. It is useful to revise the price and the cost of the above items
Views 4, 5 e 6 : to select the items to be correctly allocated in the various zones of the warehouse (receiving, shipping, etc.).
View 7: : to select items with excess space occupied compared to the picked one (space consuming items). It is useful to correctly allocate these items in locations at low or high value of space, and better estimate their transportation costs.
The ABC cross analysis, periodically executed (at least quarterly), allows to:
- Optimize the on hand inventory (in value, quantity, volume)
- Reduce the working capital
- Monitor the profitability;
- Reduce picking costs (about 50 % of the warehouse costs)
- Optimize space utilzation in warehouse and transportation.
The following indicators are also calculated:
COI (in view 5): Cube per Order Index (On hand in quantity / Picked lines)
The lower is COI, the closer to the shipping area the items are to be allocated
EAQ (in view 6): Economic Assignment Quotient (Number of lines picked / square root of picked quantities)
The higher is EAQ, the closer to the shipping area the items are to be allocated
Significant results (also inventory reduction of about 20-30 %) can be achieved in the first quarter.
For any information we are available.
View the plans